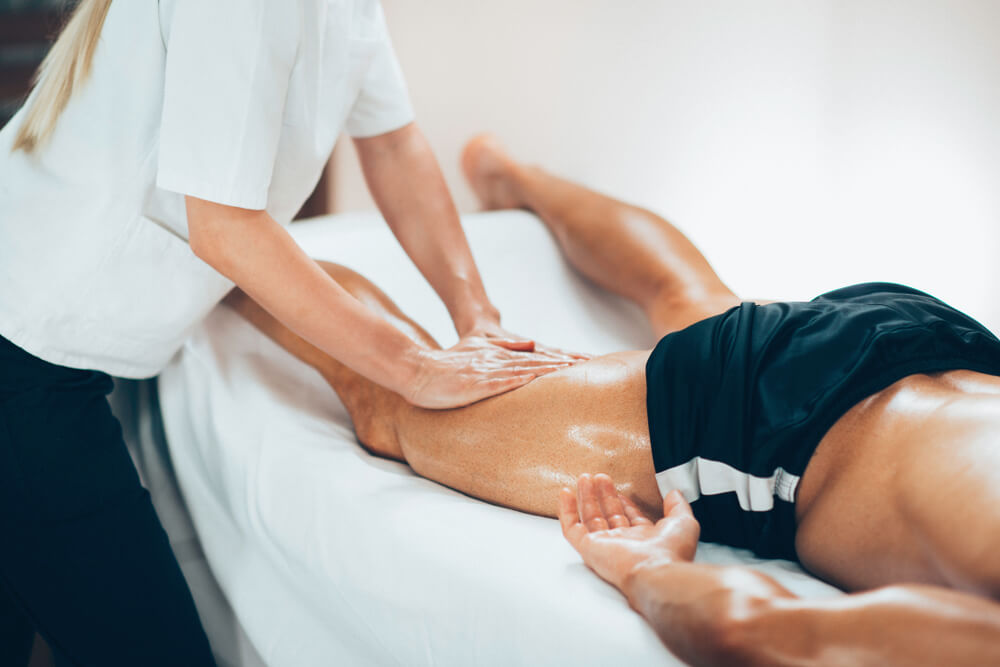
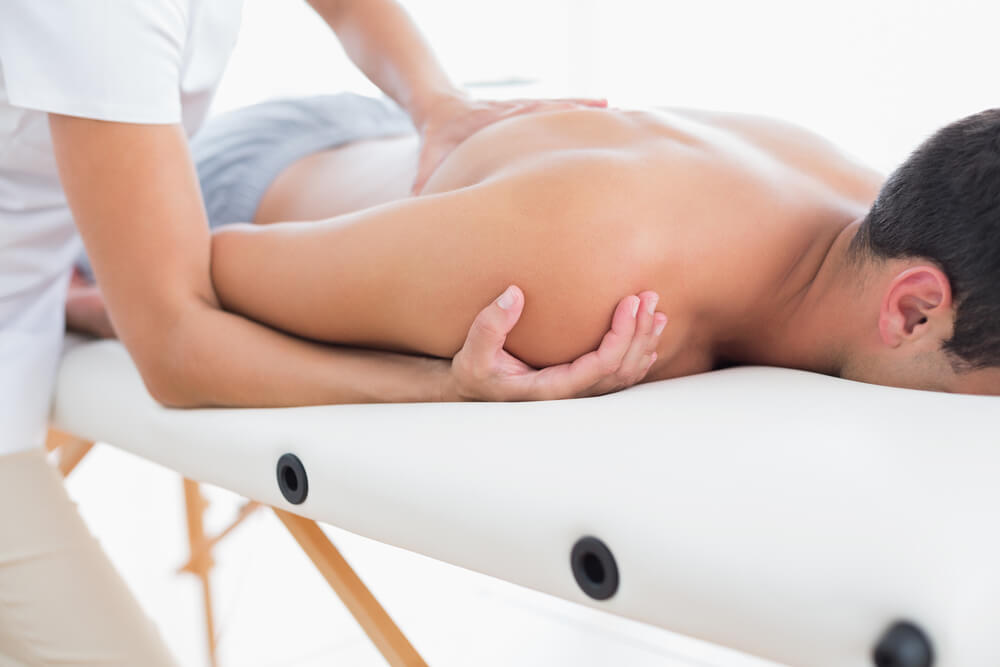
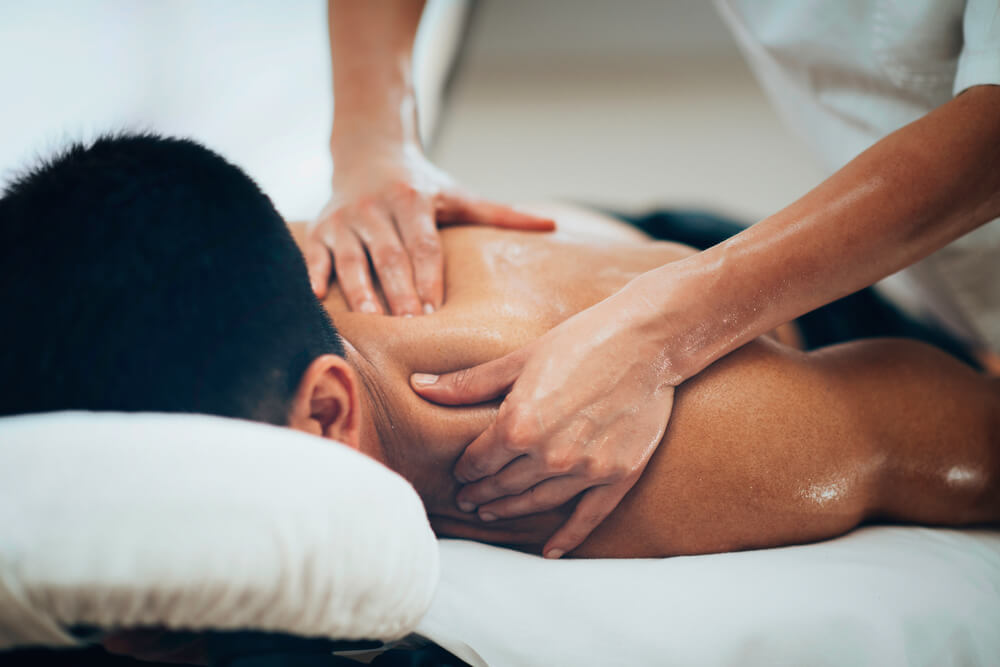
After a sporting injury, the main focus is recovery. This period can be frustrating for sporting professionals and athletes, as depending on the severity of the injury, recovery may be a slow and drawn-out process.
Massage therapy aims to reduce recovery time and speed up the healing process when supplemented with other rehabilitative methods.
There are a number of different techniques used in sports massage therapy, and the best type of massage for athletes will be determined by the injury and its severity.
Sport remedial massage therapy and its various techniques can help any sporting professional feel relief from pain while facilitating their rehabilitation. Here are some of the most common sporting-related injuries and the benefits of massage therapy for athletes.
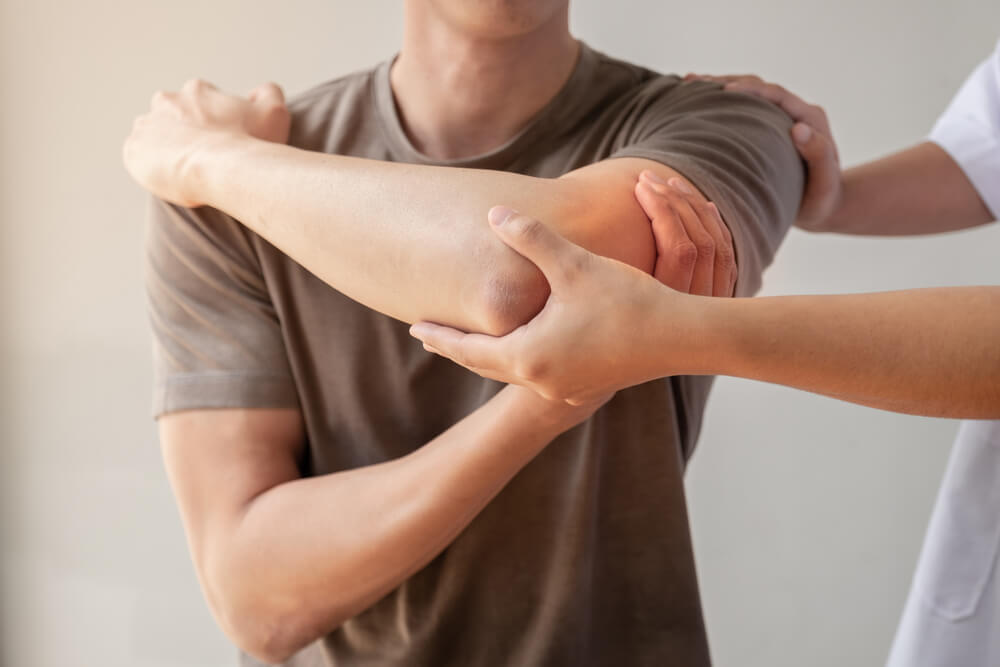
Shoulder strain
Shoulder strain or sprain is a result of injury to the shoulder ligaments or surrounding muscles.
The ligaments in your shoulder help to connect the scapula (shoulder blade), clavicle (collarbone), and sternum (breastbone) together in the shoulder joint.
Shoulder strain can occur in sports involving heavy or explosive force/contact, crashes and falls from a height, and when backward force is placed on the arm causing the stretching and tearing of the ligaments and muscles in the shoulder.
A shoulder strain is a common injury for individuals who swim, play contact sports such as rugby and football, and in sports requiring repetitive overuse of the muscles – such as tennis and golf.
Common risk factors
There are several factors that can contribute to a sports-related shoulder injury. Athletes are even more at risk of a shoulder strain or injury if they aren’t adequately warmed up or rested prior to and following a sporting session. Muscle imbalance and weakness can also lead to injury, as the shoulder takes on more load to compensate for weaknesses in areas such as the wrist or chest.
- Repetitive movement patterns: In sports such as tennis, golf, and swimming, repetitive motion in the shoulder can lead to rotator cuff tears and strain in the ligaments and muscles. As seen in cases of swimmers shoulder, or golf/tennis elbow, repetitive overhead throwing can cause the front of the shoulder to stretch and become tight, leading to muscles catching on the labrum and rotator cuff. It can also cause bursitis; a painful inflammation of the shoulder (also known as impingement syndrome).
- Fatigue: Elevated fatigue levels, repetitive use, and emotional stress can cause the shoulder muscles to overwork, leading to injury. Weak and overstretched muscles can result in frequent dislocations, ruptures, abrasions, and rotator cuff tears.
- Improper warm-up: The risk of shoulder sprain and strain is elevated in those who don’t properly warm-up before physical activity. Lifting heavy weights without warming up can lead to inflammation or tendinitis, altered tissue alignment, and poor mobility.
- Trauma: Blunt force trauma as a result of intense tackling or impact can lead to labral tears (if following a fall or direct blow to the shoulder), sprained joints and ACJ injury, fractures, cartilage tear, and separation.
Sports massage techniques for shoulders
For shoulder tendon pain treatment, sports massage therapy can be utilised.
Massage therapy has the potential to not only relieve pain in the shoulder but also encourage the healing and rehabilitation of the shoulder and surrounding muscles.
Some of the best massage techniques for shoulder pain and injury include:
- Friction technique: Using the ball of their thumb, a professional massage therapist will rub the afflicted area in circular movements. Applying friction in this way can help the breakdown of adhesions and scar tissue, helping to improve pain and range of motion in the shoulder. This along with trigger point therapy are among the best ways to treat swimmers shoulder.
- Soft tissue release: Through careful stretching and manipulation of the muscles, soft tissue release can be used to ease tissue congestion, encourage elasticity, and lengthen muscles. This can be particularly helpful in cases such as tennis elbow and overuse injuries as well as to assist in the rehabilitation process for rotator cuff injuries.
- Deep tissue massage: Using a combination of long sweeping strokes, light pressure, deep circular strokes, kneading, and shaking movements, deep tissue massage aims to release the deeper muscle fibres and assist in tension relief and muscle tightness. You can learn more about using deep tissue massage to treat shoulder pain through our hands on and online courses on offer at Discover Massage Australia.
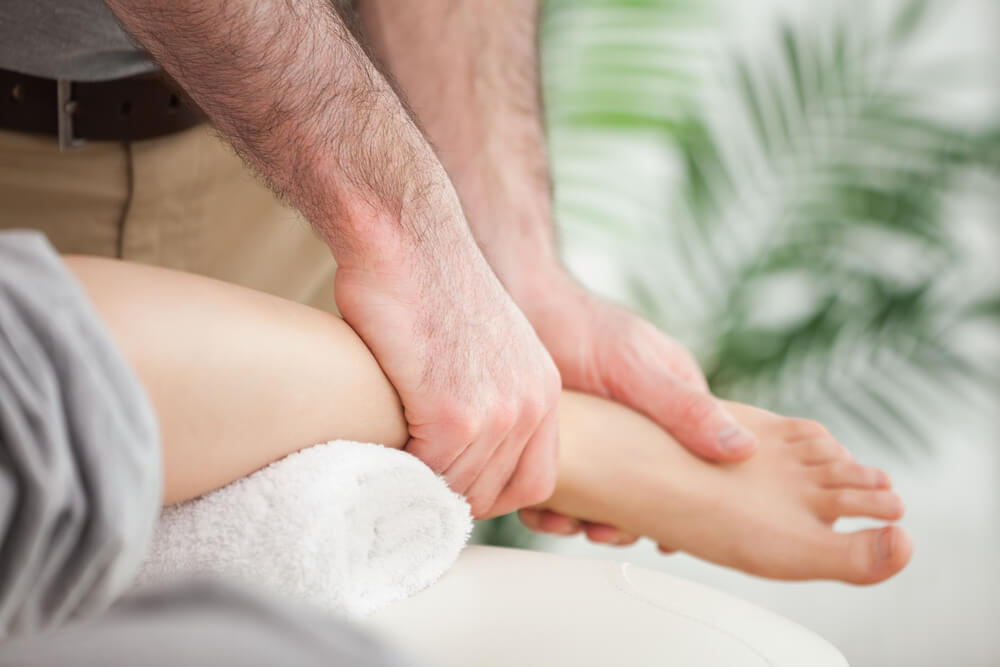
Ankle Sprain
An ankle sprain is the injury to the ligaments that support the ankle. An ankle sprain can occur if there’s a sudden twist or roll to the ankle or when planting the foot awkwardly, as well as in sports that require quick and sudden changes in direction.
An ankle sprain is a common injury for individuals who play rugby, soccer/football, tennis, basketball, and in sports such as rollerblading, ice skating, and running.
Common risk factors
- Sudden jumping, turning, twisting: In sports such as basketball, ankle injury is more predominant because of the constant jumping motion and sudden changes in direction. Ankle injury can come in the form of mild to a severe sprain as well as chronic unstable ankle that is prone to repeated injury.
- Sudden impact/trauma: A fracture or break can occur in one or more bones in the ankle when the joint sustains a sudden impact. This is more common in athletes who play sports such as rugby, football, basketball, netball, and hockey.
Sports massage for ankle sprains
In full-contact sports such as rugby, ankle sprains and fractures are more common. Ankle strain rehab requires sports massage for sprained ankles and related ankle injury. Sports massage will manage and reduce the pain in the ankle, as well as speed up an athlete’s recovery process by increasing blood flow and oxygen to the muscles. You can learn more about treating sprained ankles through Discover Massage Australia’s hands-on deep tissue massage course.
- Cross friction massage: For acute ankle sprains, cross friction massage can treat the ligaments by preventing the formation of scar tissue. This can be done 72-hours after the initial injury. The massage therapist will work the TFL (Anterior talofibular ligament), CFL (Calcaneofibular ligament) or PTFL (Posterior Talofibular ligament) through cross-fibre friction.
- Cross friction/Calf massage: From around 3 days after the injury, cross friction massage can be applied to the calf and shin muscles as well as the ankle to help loosen the muscles and improve range of motion. The massage therapist will apply direct pressure backwards and forwards using a single finger across the ligament.
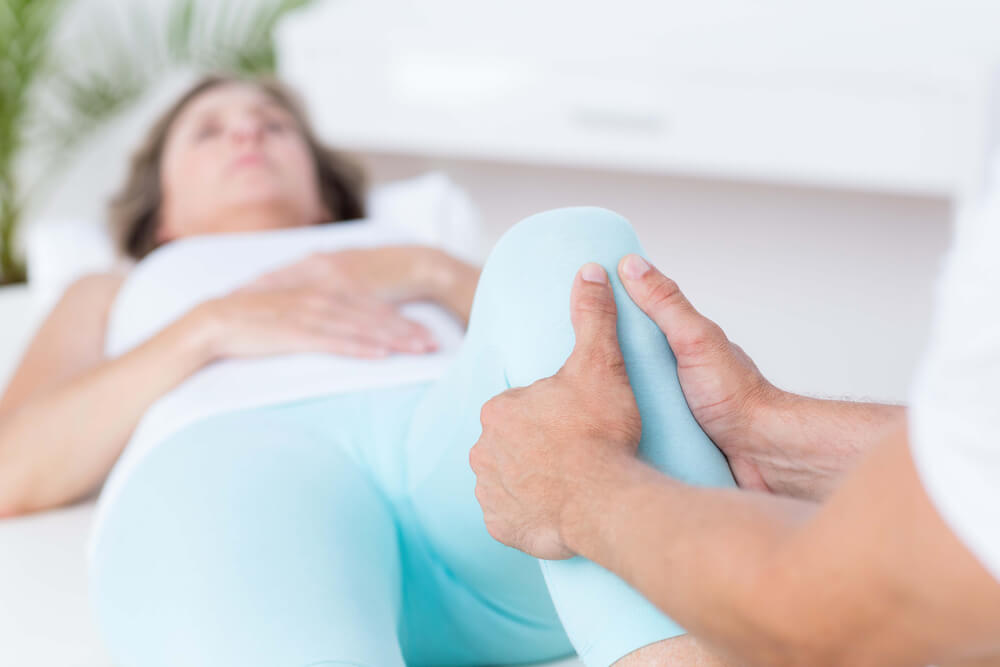
Knee Ligament Injury
There are four major ligaments in the knee. These include the Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), Medial collateral ligament (MCL), and Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Of all these ligaments, the ACL is the most common ligament to be injured from sporting activities.
The ACL is prone to being overstretched or torn from sudden twisting movements and jumping, as well as from sustaining blunt force trauma in contact sports like rugby and football.
Knee ligament injuries are a common injury for those who participate in sports such as rugby, soccer/football, skiing, surfing, and running.
Common risk factors
- Sudden jumping, turning, twisting: The ACL is often damaged in sports like rugby or soccer, where there’s a sudden twisting motion from quick and sudden directional changes. Sports like skiing and running can also cause ACL injury from awkward foot placement or landing while in motion.
- Sudden, direct impact: The ACL or PCL can be injured when there is a sudden, direct impact – either from a fall, a crash, or from direct impact with an opponent. If your outer knee is hit very hard, you may also experience an MCL tear or sprain.
Sports massage for knee pain
If you are experiencing knee pain from a sporting injury, massage therapy can assist in common tears and sprains. Medial ligament knee pain treatment and ACL knee ligament injury treatment are assisted with techniques found in sports massage therapy.
Please note that any form of deep tissue massage shouldn’t be applied while the knee injury is in its acute phase. Check with your massage therapist prior to having any form of massage applied to the knee.
- Cross friction massage: Used to treat MCL sprains, cross friction massage applies deep pressure to the ligament or tendon in a backwards and forwards motion. This allows the ligament to lay down new scar tissue and to heal. MCL massage is best done later in the rehab phase.
- Therapeutic massage: Also known as whole-body massage, athletes can benefit from the psychological effects a therapeutic massage has on their mind. Following injury, individuals can be stressed and worried about their sporting career. Therapeutic massage can be used in conjunction with a knee rehab treatment plan to maintain mental health and wellbeing.
Tennis Elbow Injury
Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow, is a common yet painful condition caused by overuse.
Unsurprisingly, tennis elbow is most common in sports such as tennis, where the repetitive movements of serving, hitting and returning the ball can lead to the inflammation or tearing of the tendons that join the forearm muscles to the outside of the elbow.
Along with sports like tennis, individuals can experience tennis elbow from participating in basketball, squash, golf, or weightlifting.
Common risk factors
- Repetitive movements, overuse: Tennis elbow symptoms usually present when there’s damage to a forearm muscle known as the Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB). This muscle helps to stabilise the wrist when the elbow is outstretched. With overuse and repeated swinging motions (such as a tennis groundstroke), the ECRB is weakened which paves the way for microscopic tears in the tendon.
How to treat tennis elbow
Tennis elbow can be effectively treated with massage therapy. Massage for tennis elbow can help to treat the injury and also prevent the injury from occurring again.
For tennis players, an emphasis on recovery between matches is needed, in order to prevent tennis elbow from interfering with their performance on the court.
- Deep tissue massage: Deep tissue massage to the forearm is effective in the easing of tennis elbow and its healing. Combined with friction therapy and soft tissue release, deep tissue massage will enhance circulation, break up scar tissue, ease pain, and improve flexibility as well as elbow strength.
- Whole body massage: For post-game and recovery in between matches, a whole-body massage for tennis elbow can help kick-start recovery and reduce fatigue. This will relax and lengthen the muscles as well as relax the mind for optimal performance on and off-court.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis or tendinitis, is a common sports-related injury, resulting in the inflammation of a tendon. Tendonitis often occurs in sports where there is overuse of the muscles or repetitive motions, and most commonly affects the elbow, wrist, finger, thigh, and shoulder.
Tendonitis is a common injury for individuals who lift weights, play rugby, tennis, swimming, basketball, bowling, golf, and baseball.
Common risk factors
- Muscle overuse, repeated motion: Tendonitis often presents in people who play sports that require repeated use or repetitive motions. For example, weightlifters may be prone to tendonitis because they are lifting heavy loads repeatedly – putting the tendon under strain and at risk of fatigue and lack of mobility.
- Sudden injury: Trauma to the affected area can result in tendonitis. For example, Achilles tendonitis may occur after a sports injury to the calf muscle and can also occur after a sudden, hard landing or fall.
Massage therapy for tendonitis
Massage is good for tendonitis, especially when it comes to shoulder tendonitis treatment and pain relief.
Since the inflammation of a single tendon can cause surrounding tendons to experience pain, using massage therapy can play a role in managing tendonitis and its repercussions on surrounding muscles, ligaments, and joints.
- Deep tissue massage: Deep tissue massage is one of the best treatments for tendonitis. Combining firm pressure and slow strokes, this massage technique reaches the deeper layers of muscle and fascia to treat chronic pain and encourage repair & recovery.
- Friction therapy: Tendonitis benefits from friction therapy massage, as it helps to break up scar tissue and allows aligned tissues to form. For best recovery results, tendonitis massage therapy should be administered as soon as possible following injury.
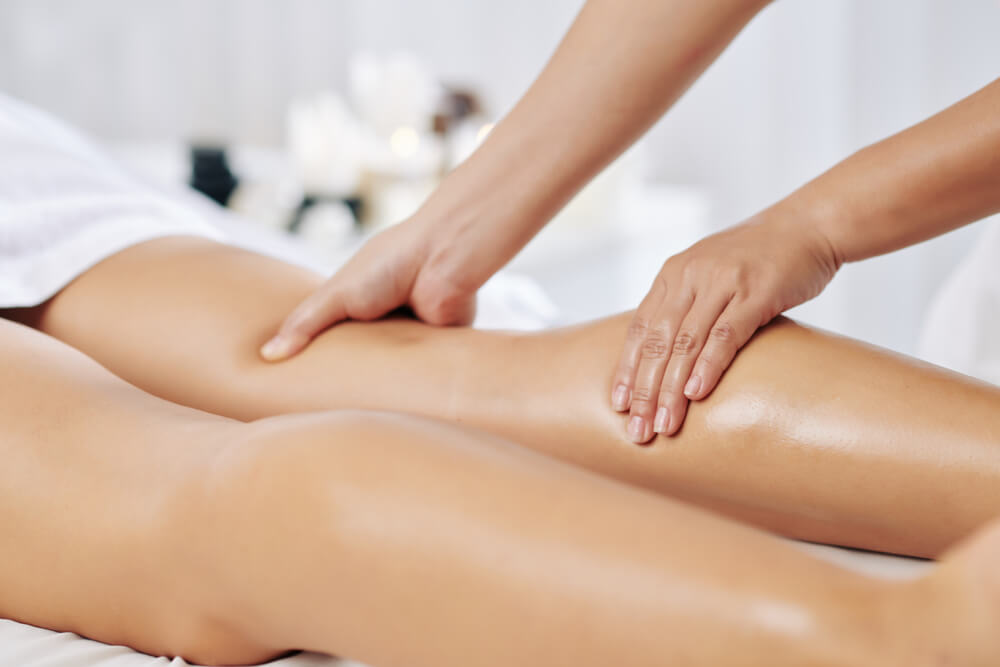
Hamstring Strain
Hamstring muscle injuries, including hamstring strain, is a frequent occurrence in athletes. Even in non-sporting professionals, a pulled hamstring is one of the more common injuries to occur when playing sport.
When you experience hamstring strain, you have injured one or more of the muscles at the back of the thigh. This happens as a result of muscles getting stretched too far to the point that they are beginning to tear.
Hamstring strains are a common injury for individuals who play sports like rugby, soccer/football, and in sports that require sprinting such as running and basketball.
Common risk factors
- Overload, overuse: Muscle overload is the most common cause of hamstring strain. This happens when the muscle is stretched beyond its capacity while ‘loaded’. This can occur when sprinting, where the muscles are lengthened and also loaded with the force of body weight required for explosive forward motion.
- Improper warm-up: Tight muscles are more likely to strain. Athletes should adequately warm up the muscles prior to intense exercise to ensure muscles are relaxed and lengthened.
- Muscle imbalance: When one muscle is stronger than its opposing muscle group, it can lead to muscle fatigue and strain. This is often the case when the hamstring muscles get tired more quickly than the quadriceps, resulting in overuse and overload of the hamstring.
Massage for hamstring strain
Sports massage therapy can be used in hamstring strain treatment and recovery. Though it shouldn’t be administered in the acute phase of the injury, massage therapy should be used in the later phase of rehabilitation to speed up the healing process and reduce pain and muscle tightness.
- Soft tissue massage: Light and superficial pressure is applied to the hamstring muscles to help break down scar tissue, relax tight muscles, and stimulate blood flow to the area. This will help speed up and aid the recovery process, and can also increase flexibility.
- Deep friction massage: As the hamstring strain injury heals, deep friction massage can be used to further facilitate recovery. Deeper work, including transverse friction, across the muscle fibers will help build healthy scar tissue. This can be done with deep lengthwise strokes and kneading, to both engage and relax the muscle.